Men: Transurethral Injection of Bulking Agents
- Urinary Incontinence and voiding dysfunction
- Men: Stress Urinary Incontinence
- Men: Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation
- Men: Transurethral Injection of Bulking Agents
- Men: Male Slings
- Men: Artificial Urinary Sphincter (AUS)
- Men: Adjustable continence device (Pro-ACT ) (Investigational)
- Women: Stress Urinary Incontinence
- Women: Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation
- Women: Transurethral Injection of Bulking Agents
- Women: Minimally Invasive Slings
- Women: Adjustable Continence Device
- Urge Incontinence in men and women
- Behavior Modification, Pelvic floor Rehabilitation and Biofeedback
- Botox Injection
- Sacral Neuromodulation
- Percutenous Tibial Nerve Simulation (PTNS)
Men: Transurethral Injection of Bulking Agents

This is an office procedure that is done under local anesthetic and patient can drive back home. It takes about 20 minutes
1- Transurethral injection of bulking agents Dr. Aboseif has an extensive experience in the transurethral injection of collagen and other bulking agents and he published one of the original article on collagen in men with incontinence after radical prostatectomy.
Collagen, the most common bulking agent used is a biologic substance that comes in a paste form and can be easily injected into body tissue and accepted by those tissues. Several other bulking agents as Duraspheres , Coaptite, macroplastiques have been recently introduced into the market.
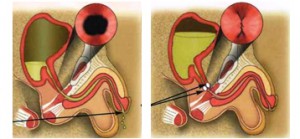
Enhance the shut-off valve of the urethra (the sphincter) to work more efficiently Procedure: Using a very special scope with a very delicate needle, 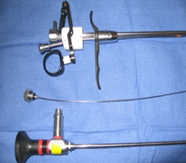 collagen is injected into the walls of the urethra at the level of the bladder neck. This causes cooptation of the urethral wall and the bladder opening and increases the resistance preventing urine from leaking out. If successful, you may need repeated injections over time to maintain incontinence as the collagen is gradually absorbed by the body.
collagen is injected into the walls of the urethra at the level of the bladder neck. This causes cooptation of the urethral wall and the bladder opening and increases the resistance preventing urine from leaking out. If successful, you may need repeated injections over time to maintain incontinence as the collagen is gradually absorbed by the body.
Aboseif, S.; O’Connell, H.; McGuire, E.: Collagen injection in postprostatectomy incontinence. J. Urol. 155: 10, 1996.